Solar Photovoltaic Market
Solar Photovoltaic Market - Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, Segmented By Application (Residential, Non-Residential and Utility), By Type (AR Coated Solar PV Glass, Tempered Solar PV Glass, TCO Coated Solar PV Glass and Others), By End-User (Crystalline Silicon PV Module, Thin Film PV Module and Perovskite Module), By Installation (Float Glass Technology and Patterne
Published Date: May - 2025 | Publisher: MIR | No of Pages: 320 | Industry: Power | Format: Report available in PDF / Excel Format
View Details Buy Now 2890 Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization| Forecast Period | 2025-2029 |
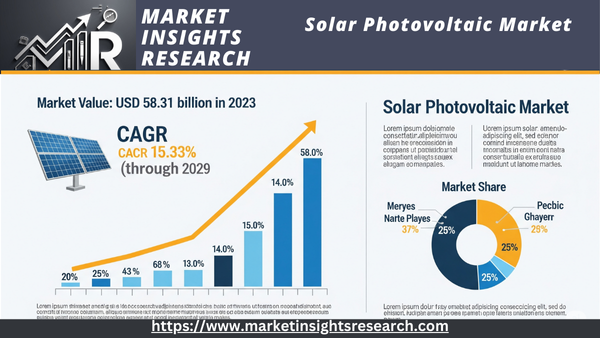
| Market Size (2023) | USD 58.31 billion |
| CAGR (2024-2029) | 17.33% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | Float Glass Technology |
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
| Market Size (2023) | USD 138.52 billion |
Market Overview
Global Solar Photovoltaic Market was valued at USD 58.31 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to project robust growth in the forecast period with a CAGR of 15.33% through 2029. International climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, have set the stage for aggressive carbon reduction targets. Countries that are signatories to these agreements are pressured to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. Solar PV is a key component of their strategies to transition to low-carbon energy sources and meet these targets.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Key Market Drivers
Environmental Concerns and Climate Change Mitigation
The global solar photovoltaic (PV) market has experienced remarkable growth recently, driven by a confluence of factors. One of the most significant drivers of this growth is the increasing concern about environmental issues and the urgent need to mitigate climate change. As the world grapples with the consequences of excessive greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to clean and renewable energy sources has become a top priority.
Solar PV technology is at the forefront of this transition. It generates electricity by harnessing the power of the sun, producing no direct emissions or air pollutants during operation. This eco-friendly aspect of solar PV makes it an attractive choice for both governments and individuals looking to reduce their carbon footprint. The environmental benefits of solar energy are increasingly recognized, leading to a surge in demand for solar PV installations globally.
Governments and international organizations are also playing a crucial role in promoting the adoption of solar PV. Many countries have established ambitious renewable energy targets and incentives, such as feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and subsidies, to encourage the deployment of solar PV systems. In addition, global climate agreements like the Paris Agreement have set the stage for aggressive carbon reduction targets, further emphasizing the importance of solar PV in the transition to clean energy.
The first driver of the global solar PV market is the growing concern about environmental issues and the need to mitigate climate change. Solar PV technology aligns perfectly with these objectives by providing a clean and sustainable source of energy, and this alignment is propelling the industry's expansion worldwide.
Technological Advancements and Cost Reduction
The global solar photovoltaic (PV) market has witnessed significant growth due to ongoing technological advancements and the substantial reduction in the cost of solar PV systems. These developments have made solar energy more accessible and competitive in the energy market, driving its widespread adoption.
Technological advancements in solar PV have resulted in the increased efficiency, durability, and versatility of solar panels. Improvements in materials, such as the development of high-efficiency solar cells like PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) and bifacial panels, have enhanced the performance of solar PV systems. Additionally, innovations in energy storage and grid integration technologies have addressed some of the challenges associated with solar's intermittent nature, making it a more reliable and versatile energy source.
One of the most critical factors in the growth of the solar PV market has been the substantial reduction in the cost of solar panels and associated components. The economies of scale, increased competition, and improved manufacturing processes have led to a significant decline in the cost of solar PV systems over the past decade. This cost reduction has made solar energy more economically viable and competitive with traditional fossil fuels, particularly in regions with abundant sunlight.
Government policies and incentives have also played a role in driving down the cost of solar PV installations. Subsidies, tax credits, and net metering programs can significantly reduce the upfront costs for homeowners and businesses, further incentivizing the adoption of solar technology. These factors have made solar PV systems a financially attractive choice, not only for environmentally conscious individuals but also for businesses and utility companies looking to reduce energy costs and improve their environmental credentials.
Technological advancements and cost reduction are crucial drivers of the global solar PV market. These factors have made solar energy more efficient, affordable, and accessible, spurring its rapid adoption and growth.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Energy Security and Energy Independence
Energy security and independence are becoming increasingly important considerations for nations around the world. Solar photovoltaic (PV) technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing these aspects, which, in turn, drives the growth of the global solar PV market.
Energy security refers to a nation's ability to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply. Relying on fossil fuels, which often involve international trade and geopolitical complexities, can make a country vulnerable to energy supply disruptions. Solar PV systems can provide a degree of energy security by generating electricity locally, reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. This benefit is particularly relevant in regions where energy resources are scarce, and solar energy can fill the gap.
Energy independence, on the other hand, refers to a country's ability to produce its energy, reducing its dependence on external sources. Solar PV technology empowers nations to harness their own abundant solar resources to generate electricity. The process bolsters energy independence and helps diversify the energy mix, reducing exposure to the volatility of fossil fuel prices.
Governments and policymakers recognize the significance of solar PV in enhancing energy security and independence, and as a result, they are implementing policies and incentives to promote the adoption of solar technology. This process includes incentivizing residential and commercial solar installations, as well as supporting large-scale solar projects to boost the domestic energy supply.
Solar PV's role in energy security and independence is not limited to national scales; it extends to microgrids and off-grid solutions, which are crucial for providing reliable power in remote areas and during emergencies. The resilience and decentralized nature of solar PV installations make them a valuable asset in ensuring continuous energy availability, even in adverse conditions.
Energy security and independence are key drivers of the global solar PV market. Solar PV technology offers nations the opportunity to reduce their reliance on external energy sources and bolster their energy security, contributing to the industry's expansion and development.
Key Market Challenges
Environmental Concerns and Climate Change Mitigation
The global solar photovoltaic (PV) market has experienced remarkable growth recently, driven by a confluence of factors. One of the most significant drivers of this growth is the increasing concern about environmental issues and the urgent need to mitigate climate change. As the world grapples with the consequences of excessive greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to clean and renewable energy sources has become a top priority.
Solar PV technology is at the forefront of this transition. It generates electricity by harnessing the power of the sun, producing no direct emissions or air pollutants during operation. This eco-friendly aspect of solar PV makes it an attractive choice for both governments and individuals looking to reduce their carbon footprint. The environmental benefits of solar energy are increasingly recognized, leading to a surge in demand for solar PV installations globally.
Governments and international organizations are also playing a crucial role in promoting the adoption of solar PV. Many countries have established ambitious renewable energy targets and incentives, such as feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and subsidies, to encourage the deployment of solar PV systems. In addition, global climate agreements like the Paris Agreement have set the stage for aggressive carbon reduction targets, further emphasizing the importance of solar PV in the transition to clean energy.
The first driver of the global solar PV market is the growing concern about environmental issues and the need to mitigate climate change. Solar PV technology aligns perfectly with these objectives by providing a clean and sustainable source of energy, and this alignment is propelling the industry's expansion worldwide.
Technological Advancements and Cost Reduction
The global solar photovoltaic (PV) market has witnessed significant growth due to ongoing technological advancements and the substantial reduction in the cost of solar PV systems. These developments have made solar energy more accessible and competitive in the energy market, driving its widespread adoption.
Technological advancements in solar PV have resulted in the increased efficiency, durability, and versatility of solar panels. Improvements in materials, such as the development of high-efficiency solar cells like PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) and bifacial panels, have enhanced the performance of solar PV systems. Additionally, innovations in energy storage and grid integration technologies have addressed some of the challenges associated with solar's intermittent nature, making it a more reliable and versatile energy source.
One of the most critical factors in the growth of the solar PV market has been the substantial reduction in the cost of solar panels and associated components. The economies of scale, increased competition, and improved manufacturing processes have led to a significant decline in the cost of solar PV systems over the past decade. This cost reduction has made solar energy more economically viable and competitive with traditional fossil fuels, particularly in regions with abundant sunlight.
Government policies and incentives have also played a role in driving down the cost of solar PV installations. Subsidies, tax credits, and net metering programs can significantly reduce the upfront costs for homeowners and businesses, further incentivizing the adoption of solar technology. These factors have made solar PV systems a financially attractive choice, not only for environmentally conscious individuals but also for businesses and utility companies looking to reduce energy costs and improve their environmental credentials.
Technological advancements and cost reduction are crucial drivers of the global solar PV market. These factors have made solar energy more efficient, affordable, and accessible, spurring its rapid adoption and growth.
Energy Security and Energy Independence
Energy security and independence are becoming increasingly important considerations for nations around the world. Solar photovoltaic (PV) technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing these aspects, which, in turn, drives the growth of the global solar PV market.
Energy security refers to a nation's ability to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply. Relying on fossil fuels, which often involve international trade and geopolitical complexities, can make a country vulnerable to energy supply disruptions. Solar PV systems can provide a degree of energy security by generating electricity locally, reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. This benefit is particularly relevant in regions where energy resources are scarce, and solar energy can fill the gap.
Energy independence, on the other hand, refers to a country's ability to produce its energy, reducing its dependence on external sources. Solar PV technology empowers nations to harness their own abundant solar resources to generate electricity. The process not only bolsters energy independence but also helps diversify the energy mix, reducing exposure to the volatility of fossil fuel prices.
Governments and policymakers recognize the significance of solar PV in enhancing energy security and independence, and as a result, they are implementing policies and incentives to promote the adoption of solar technology. This process includes incentivizing residential and commercial solar installations, as well as supporting large-scale solar projects to boost the domestic energy supply.
Solar PV's role in energy security and independence is not limited to national scales; it extends to microgrids and off-grid solutions, which are crucial for providing reliable power in remote areas and during emergencies. The resilience and decentralized nature of solar PV installations make them a valuable asset in ensuring continuous energy availability, even in adverse conditions.
Energy security and independence are key drivers of the global solar PV market. Solar PV technology offers nations the opportunity to reduce their reliance on external energy sources and bolster their energy security, contributing to the industry's expansion and development.
Key Market Trends
Increasing Adoption of Bifacial Solar Panels
One notable trend in the global solar photovoltaic (PV) market is the increasing adoption of bifacial solar panels. Bifacial solar panels are designed to capture sunlight on both the front and rear sides, which enhances their energy generation capabilities. Several factors are driving this technology trend, which is reshaping the solar PV industry.
The primary advantage of bifacial solar panels is their improved energy yield. These panels can capture sunlight that is reflected from the ground or nearby surfaces, in addition to the direct sunlight they receive on the front side. This increased light capture leads to higher electricity production, making bifacial panels a cost-effective choice for solar projects seeking to maximize energy output in various environments.
Bifacial panels are versatile and can be used in various solar installations. They are suitable for utility-scale solar farms, residential rooftop systems, and commercial solar projects. As a result, bifacial technology has broad applicability, which has contributed to its growing popularity.
Technological advancements and cost reductions in bifacial panel manufacturing have made these panels more accessible and affordable. The industry is witnessing increased research and development efforts focused on improving the efficiency and durability of bifacial panels. These advancements, coupled with economies of scale, are contributing to the decreasing cost of bifacial solar panels, making them a viable option for a wider range of solar projects.
The shift toward bifacial panels also aligns with the industry's sustainability goals. By increasing energy yield, bifacial panels can reduce the amount of land required for solar installations, minimizing land-use conflicts and environmental impacts. Moreover, the trend toward bifacial technology aligns with the broader industry goal of increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of solar PV systems, helping to further promote the adoption of clean energy.
The increasing adoption of bifacial solar panels is a significant trend in the global solar PV market. The panels' improved energy yield, versatility, cost reductions, and sustainability benefits drive this trend. This trend is likely to continue to reshape the solar PV industry and contribute to its ongoing growth.
Integrated Energy Systems and Microgrids
Another emerging trend in the global solar photovoltaic (PV) market is the development and deployment of integrated energy systems and microgrids. This trend is driven by the desire for greater energy resilience, grid independence, and the need to effectively manage renewable energy resources, especially in remote or off-grid areas.
Integrated energy systems refer to the combination of various energy sources, including solar PV, wind, energy storage, and other distributed energy resources. These systems are designed to work together to provide a reliable and sustainable energy supply, reducing dependence on centralized grids. Integrated energy systems are becoming increasingly common in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Microgrids are a subset of integrated energy systems and are essentially smaller, localized grids that can operate independently or in coordination with the main grid. They are particularly valuable in areas where grid reliability is a concern or where communities and businesses seek to reduce their environmental impact and energy costs.
Solar PV plays a central role in these integrated systems and microgrids. As the cost of solar PV continues to decline and technology advances, solar panels are often the primary source of electricity generation in these setups. The surplus energy generated by solar panels can be stored in batteries and used when sunlight is not found, ensuring a consistent power supply. Moreover, solar PV can be combined with other renewable sources, such as wind or hydropower, to create a diverse and reliable energy mix.
Advancements in energy management and control systems have also contributed to the rise of integrated energy systems and microgrids. These systems use sophisticated software to optimize energy generation, storage, and consumption, making it possible to effectively manage energy resources and maintain grid stability.
Government incentives and regulatory support for microgrid development, especially in remote or underserved regions, have further accelerated this trend. By providing financial incentives and streamlining the regulatory process, governments are promoting the adoption of integrated energy systems and microgrids, which, in turn, stimulates the demand for solar PV installations.
The trend of integrated energy systems and microgrids in the global solar PV market reflects the industry's drive toward greater energy resilience, sustainability, and grid independence. As technology advances and policy support grows, this trend is likely to continue shaping the future of energy distribution and consumption.
Segmental Insights
End-User
The Crystalline Silicon PV Module segment
Crystalline Silicon PV modules, often referred to as c-Si modules, are solar panels that use crystalline silicon as the semiconductor material. They are categorized into two main typesmonocrystalline and polycrystalline, both of which have similar principles of operation but differ in their manufacturing processes and efficiency levels.
Economies of scale, improved production processes, and increased competition in the solar industry have contributed to cost reductions. This trend has made solar energy more accessible and competitive with conventional energy sources. These innovations in the c-Si module design help reduce the impact of shading, minimize electrical losses, and enhance the overall reliability of the modules.
Crystalline Silicon PV modules are known for their high energy conversion efficiency. Monocrystalline modules, in particular, offer some of the highest efficiencies found in the market. This high efficiency is a significant driver of growth, as it allows for greater energy production from a given area of solar panels, making c-Si modules an attractive choice for maximizing energy yield in limited spaces.
The trend of bifacial solar panels, which can capture sunlight from both the front and rear sides, has extended to c-Si modules. This combination with bifacial technology increases energy production and creates new ways to make better use of available space, like using raised structures or solar canopies.
Crystalline Silicon PV modules are a cornerstone of the global solar PV market, offering high efficiency, reliability, and cost-competitiveness. As technology and manufacturing processes continue to evolve, these modules are expected to maintain their dominance while addressing sustainability concerns and embracing innovative design trends to further enhance their performance and market presence.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific emerged as the dominant region in 2023, holding the largest market share. The Asia-Pacific region is characterized by its diversity, both in terms of solar PV installations and market dynamics. It encompasses developed economies like Japan and Australia, rapidly industrializing countries like China and India, and a range of smaller nations with varying levels of solar PV adoption. The region plays a pivotal role in the global solar PV market due to its sheer scale and potential for growth.
Many countries in the Asia-Pacific region have implemented strong policy support and financial incentives to promote solar PV adoption. Feed-in tariffs, net metering, tax incentives, and renewable energy targets have been pivotal in encouraging investments in solar PV projects.
The cost of solar PV technology has continued to decline, making it an attractive choice for energy generation. This cost reduction has been instrumental in the rapid adoption of solar PV across the region, particularly in densely populated countries with high energy demand.
The Asia-Pacific region has witnessed significant growth in utility-scale solar PV projects. These projects, often in the form of solar farms or solar parks, provide a substantial amount of electricity to the grid. Countries like China and India have been leaders in this trend.
The Asia-Pacific region is a significant player in the global solar PV market, driven by supportive policies, falling costs, and a growing commitment to sustainability. The region's diverse landscape presents both opportunities and challenges, and as technology and policies continue to evolve, the solar PV market in Asia-Pacific is expected to see continued growth and transformation.

Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Recent Developments
- First Solar made headlines in June 2024 by revealing that its Series 6 Plus and Series 7 TR1 photovoltaic (PV) solar modules have attained the prestigious EPEAT Climate+ designation, marking a groundbreaking achievement in the solar technology and manufacturing sector.
Key Market Players
- Xinyi Solar Holdings Ltd.
- IRICO Group New Energy Co., Ltd.
- Wuxi Suntech Power Co., Ltd.
- Qingdao Jinxin Glass Co., Ltd.
- Dongguan CSG Solar Glass Co., Ltd.
- Nippon Sheet Glass Co., Ltd.
- Taiwan Glass Ind. Corp.
- Borosil Renewables Ltd.
- Corporación Acciona Energías Renovables, S.A.
- Hecker Glastechnik Gmbh & Co. Kg
|
By Application |
By Type |
By End-User |
By Installation |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
|
Related Reports
- Commercial Hot Water Boiler Market Size - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Technology (Condensing, Non-Con...
- UK Commercial Boiler Market Size By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity, By Technology (Condensing, Non...
- Residential Electric Boiler Market Size - By Voltage Rating (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage), Industry Analysis Report, Reg...
- Europe Steam Boiler Market - By Capacity, By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal), By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condensing), ...
- Electric Boiler Market Size By Voltage Rating (Low, Medium), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Food P...
- Europe Boiler Market By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
Table of Content
-
Executive Summary
-
1.1 Market Overview
-
1.2 Key Trends and Insights
-
1.3 Strategic Recommendations
-
-
Introduction
-
2.1 Report Objectives
-
2.2 Scope and Definitions
-
2.3 Methodology and Data Sources
-
2.4 Assumptions and Limitations
-
-
Market Overview
-
3.1 Solar PV Technology Overview
-
3.2 Role in Global Energy Transition
-
3.3 Value Chain and Market Structure
-
3.4 Comparison with Other Renewable Technologies
-
-
Market Dynamics
-
4.1 Drivers
-
4.1.1 Declining Costs of Solar Modules
-
4.1.2 Government Incentives and Net Metering Policies
-
4.1.3 Growing Corporate Sustainability Commitments
-
-
4.2 Restraints
-
4.2.1 Intermittency and Grid Integration Issues
-
4.2.2 Land Use and Environmental Concerns
-
-
4.3 Opportunities
-
4.3.1 Floating Solar and Agri-PV Systems
-
4.3.2 Solar + Storage Integration
-
-
4.4 Market Challenges
-
4.5 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
-
Technology Landscape
-
5.1 Crystalline Silicon (Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline)
-
5.2 Thin Film Technologies (CdTe, CIGS, a-Si)
-
5.3 Emerging Technologies (Perovskite, Bifacial, Tandem Cells)
-
5.4 Inverters, Mounting Systems, and Tracking Technologies
-
-
Market Segmentation
-
6.1 By Installation Type
-
6.1.1 Ground-Mounted
-
6.1.2 Rooftop (Residential, Commercial)
-
6.1.3 Floating Solar
-
-
6.2 By Grid Type
-
6.2.1 Grid-Connected
-
6.2.2 Off-Grid and Hybrid Systems
-
-
6.3 By End-User
-
6.3.1 Utility
-
6.3.2 Commercial & Industrial
-
6.3.3 Residential
-
6.3.4 Agricultural
-
-
-
Regional Analysis
-
7.1 North America
-
7.2 Europe
-
7.3 Asia-Pacific
-
7.4 Latin America
-
7.5 Middle East & Africa
-
-
Market Size and Forecast (2020–2030)
-
8.1 Global Installed Capacity Forecast
-
8.2 Revenue Forecast by Region and Segment
-
8.3 Solar PV Demand Outlook by End-Use
-
-
Competitive Landscape
-
9.1 Market Share of Major Players
-
9.2 Key Company Profiles
-
9.2.1 JinkoSolar
-
9.2.2 Trina Solar
-
9.2.3 First Solar
-
9.2.4 Canadian Solar
-
9.2.5 LONGi Green Energy
-
9.2.6 Others
-
-
9.3 Strategic Developments, Joint Ventures, and Expansions
-
-
Policy and Regulatory Framework
-
10.1 Global and Regional Renewable Energy Targets
-
10.2 Subsidies, Tariffs, and FiT Programs
-
10.3 Land Use and Environmental Approval Processes
-
-
Trends and Innovation Outlook
-
11.1 Digital Monitoring and Smart Inverters
-
11.2 AI and Predictive Maintenance in Solar Farms
-
11.3 ESG-Driven Solar Investments and Green Financing
-
-
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
-
Appendices
-
13.1 Glossary
-
13.2 Research Methodology
-
13.3 Sources and References
-
To get a detailed Table of content/ Table of Figures/ Methodology Please contact our sales person at ( chris@marketinsightsresearch.com )
FAQ'S
For a single, multi and corporate client license, the report will be available in PDF format. Sample report would be given you in excel format. For more questions please contact:
Within 24 to 48 hrs.
You can contact Sales team (sales@marketinsightsresearch.com) and they will direct you on email
You can order a report by selecting payment methods, which is bank wire or online payment through any Debit/Credit card, Razor pay or PayPal.
Discounts are available.
Hard Copy
